In this article, we’ll explain the key Arrow GNSS receiver features, including unique attributes across models, physical description, and main components.
Helpful Tips to Compare Arrow Series Features and Models
When selecting an Arrow GNSS model, it’s important to first note the available four models:
- Arrow Lite® — Submeter GPS receiver (accesses only the U.S. GPS constellation)
- Arrow 100® — Submeter GNSS receiver (accesses all four global GNSS constellations)
- Arrow 200® — Centimeter-level GNSS receiver (accesses all four global GNSS constellations and also offers RTK compatibility)
- Arrow Gold® — Centimeter-level GNSS receiver (accesses all four global GNSS constellations and also offers RTK compatibility with the maximum channels and frequencies of any Arrow model for greatest productivity in the field; also includes proprietary SafeRTK® for when signal is lost)

How to understand popular terms related to your Arrow GNSS receiver
When exploring GNSS receivers for the first time, the number and type of various acronyms can be overwhelming. Here are some simplified definitions of important acronyms and other terminology related to Arrow GNSS receivers:
- Constellations: Constellation refers to a group of satellites. In the world of high-accuracy positioning, these satellite groups are called GNSS constellations. There are several GNSS constellations maintained by government organizations worldwide. Some are geostationary, and others orbit.
- GNSS: GNSS stands for “Global Navigation Satellite System.” GPS is probably the most popular GNSS constellation in the world, because it was the first. Here is a fascinating article from Interesting Engineering about the history of the GPS constellation. There are other GNSS constellations that Arrow GNSS receivers (models 100, 200, and Gold) work with including these: Galileo (European Union constellation), GLONASS (Russian constellation), BeiDou (Chinese constellation), QZSS (Japanese constellation)
- Differential Corrections Source: Each Arrow GNSS receiver is capable of being used with various differential corrections sources. The application of a differential correction, and the specific way in which a GNSS receiver processes the differential correction data, is a large part of what allows users to achieve a much higher accuracy than is available with consumer GPS receivers.
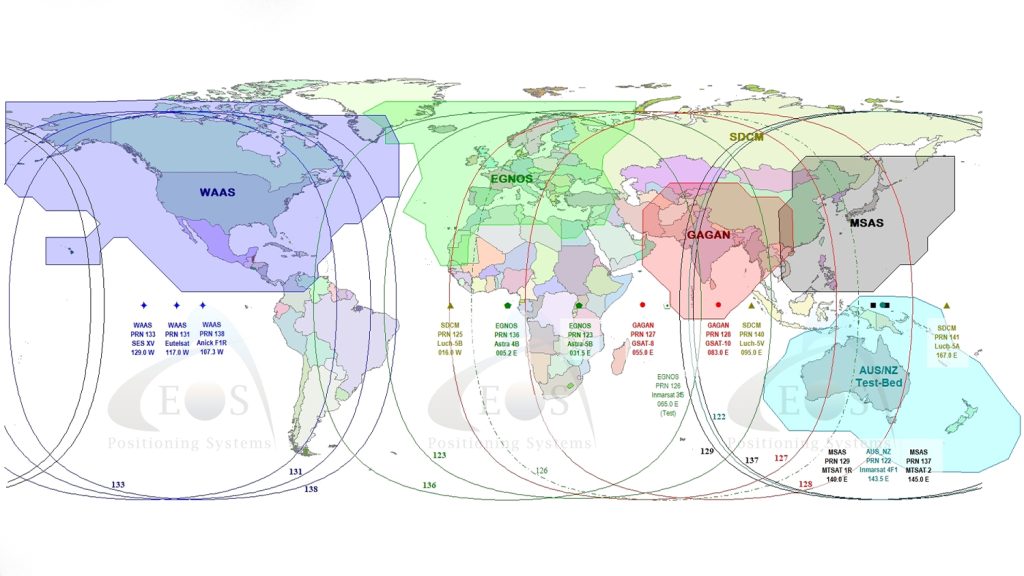
- SBAS: SBAS stands for “Satellite Based Augmentation System.” It is a type of differential corrections source that can get about 30-60cm horizontal accuracy. Similar to GNSS constellations, SBAS systems are typically installed, owned, and operated by government organizations and their contractors. SBAS works only in and around the government(s) that have installed them. For information on an SBAS in your area, consult this article all about SBAS. In short, these are the current operational SBAS systems in 2021: WAAS (can be used in the U.S., Canada, and some parts of Latin America); EGNOS (Europe); MSAS (Japan); GAGAN (India). All Arrow GNSS receivers can work with SBAS, but it is recommended for Arrow 100 and Arrow Lite models.
- RTK: RTK stands for “Real-Time Kinematic.” It is another source of differential corrections. RTK networks allow a GNSS receiver to achieve centimeter-level accuracy. The availability of RTK networks depend on the region in which your mobile work is taking place. Eos can help you determine if there is a free or paid RTK network available in your region. For customers in the United States, this is a helpful article from GPS World showing all public/free RTK networks.
- Base Station: A base station is a privately or publicly owned single reference station that provides a source of differential corrections to compatible GNSS receivers. The Arrow Gold and Arrow 200 can work with existing base stations, or you can purchase an extra Arrow Gold to be used as a base station. A base station can be permanently installed, such as on a roof, or it can be mobile, meaning it is able to be moved from region to region and used when survey-grade accuracy required. Base stations are a good option for teams who need to perform centimeter-level mobile work in areas where there is no free RTK network. That is what this utility organization did in rural Canada to perform tracking and traceability.
- Atlas®: Atlas® is a paid, subscription-based source of differential corrections. It uses LBand radio to provide differential correction services for worldwide, real-time submeter, subfoot or sub-decimeter positioning. Subscriptions are available in a variety of lengths. Eos can help you obtain an Atlas® subscription if it is the best fit for your needs. Customers can also request a free three-day trial of Atlas® by contacting Eos technical support. It is best to consult with Eos directly to determine if an Atlas® subscription is the best solution for your needs. Learn more about Atlas® here.
How to understand popular terms related to your Arrow GNSS receiver
Some additional, miscellaneous terms you may see related to your Arrow GNSS receiver are explained briefly below. If you have questions on any feature or term related to your Arrow GNSS receiver, please contact our team. We are happy to help!
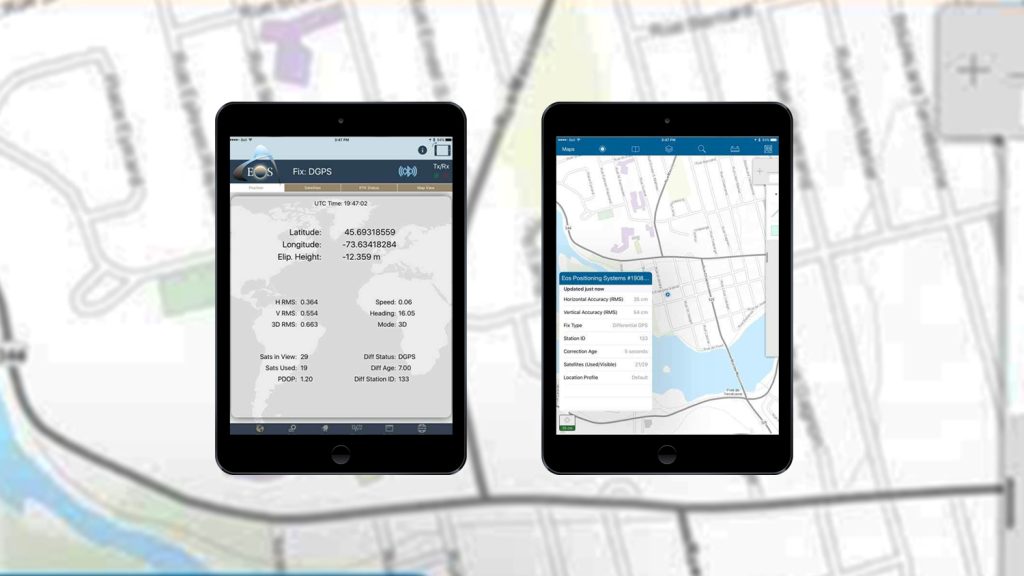
- Raw measurement output (via documented binary messages) or RINEX converter
- Position and raw measurement update rates: Of up to optional 10Hz or 20Hz
- COAST™ technology provides consistent performance with old correction data and guarantees an all-day DGPS/DGNSS solution even in forestry applications (with suitable SBAS or Atlas® coverage)
- Optional Auto-Dif: A base station-free way of differentially positioning for submeter applications
- Base Station Support: Support base and rover modes
- Universal Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR: (supported profiles: iAP for Apple iOS® and SPP for Windows and Android) Ensures compatibility with any up-to-date handheld/tablet/computer/smartphone and software combination
- One USB 2.0 compliant port can be used for configuration, or to output/receive RTCM corrections and/or NMEA messages
- Integrated, field-replaceable Smart Li-Ion battery with built-in charger for full day operation
Finally, this comparison chart offers a more succinct demonstration of the Arrow Series® capabilities as well as the differences between models.