Costa Rica’s Coopeguanascaste Digitally Transforms Electric Distribution with ArcGIS and Eos GNSS
Coopeguanacaste is an electric cooperative that serves over 90,000 members across the rural Guanacaste region of Costa Rica — making it the country’s second-largest electric provider. Established in 1965 to meet a critical need for electricity, Coopeguanacaste has grown significantly, but now faces a new challenge: sustainable scalability.

The Challenge: Scalability
Growing from just 229 members in 1965 to over 90,000 today, Coopeguanacaste now covers a whopping 3,696 km². Recently, Coopeguanacaste achieved 100% renewable energy generation with its hydroelectric, solar, and wind projects, yet inefficiencies, outdated data, and increasing demand still hindered its distribution services.
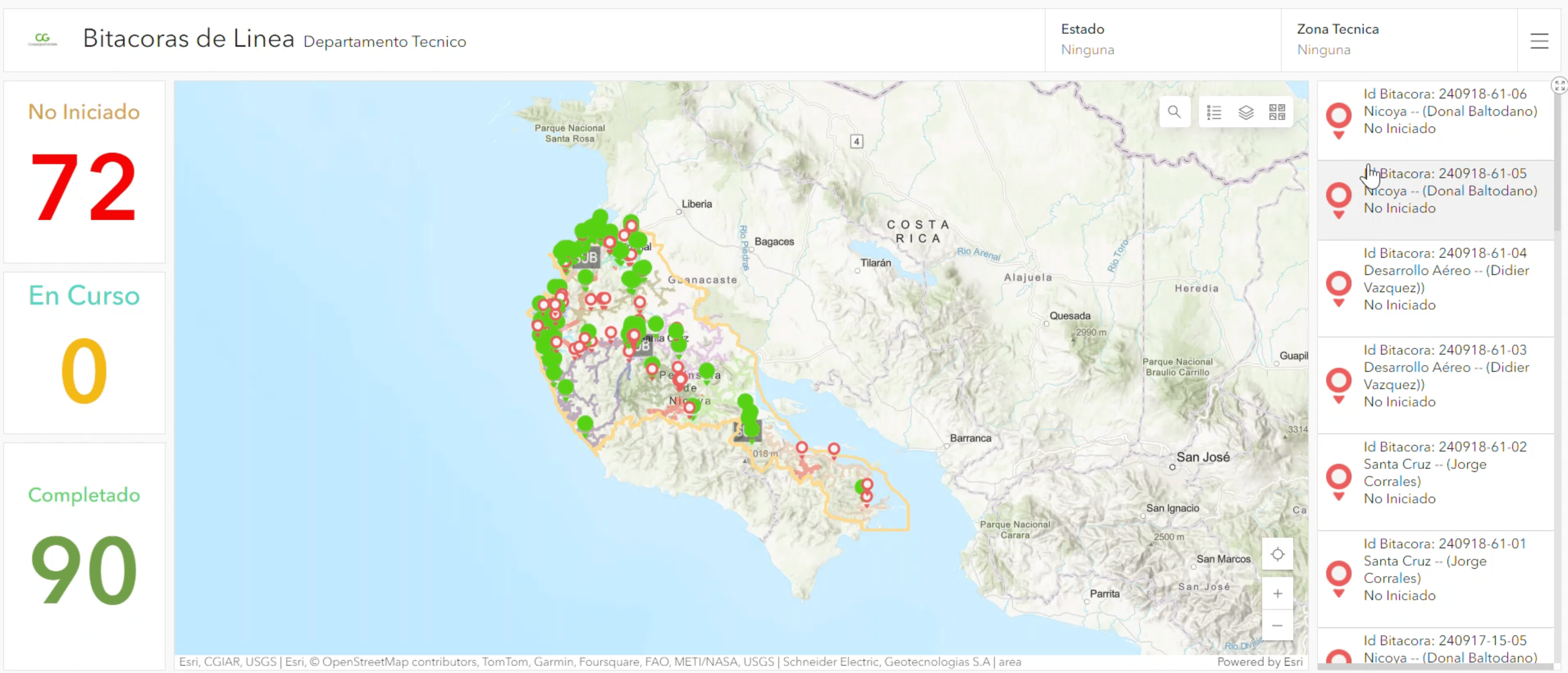
The cooperative relied on paper records, outdated digital tools, and imprecise data, challenging its financial stability and creating discrepancies between asset data and enterprise resource planning (ERP) records. These issues complicated annual reports required by the Public Services Regulatory Authority (ARESEP) for rate adjustments, underscoring the need for digital modernization.
“Those of us working on the systems side of operations have been increasingly challenged,” explained Coopeguanacaste GIS Systems Administrator Mario Cabalceta.
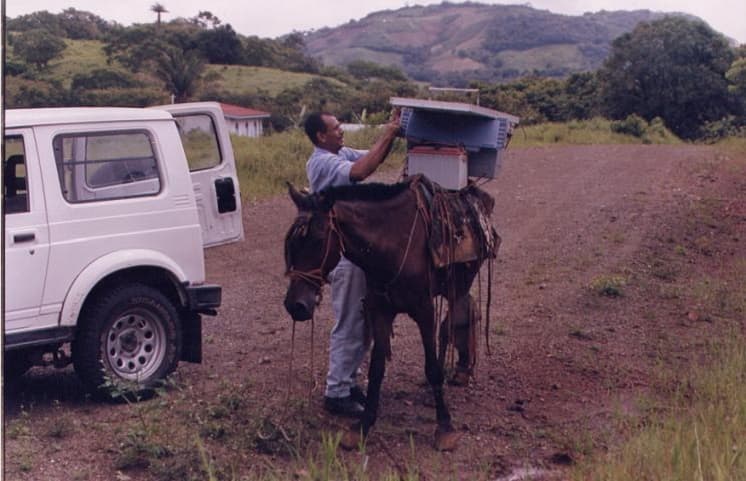

The Solution: Improved Accuracy and an Integrated GIS
In 2023, Coopeguanacaste hired Esri partner NimbusTech to implement a modern geographic information system (GIS) with ArcGIS®. One initial difficulty was convincing the cooperative’s management that Esri’s ArcGIS platform was the right choice. Coopeguanacaste had access to other free software and systems and lacked staff training in ArcGIS software. However, the free software didn’t allow for integration with other business and asset-management systems, and NimbusTech proved able to both deploy the systems and train utility staff.
“We have begun an incredibly important growth process,” Cabalceta said.
“The integration of Eos Positioning Systems’ equipment with ArcGIS Survey123 and ArcGIS Field Maps has been crucial for updating the network assets. This proved to be the most effective and cost-efficient option for our client to create an accurate digital twin of their electric system.”
— Clara Abellan, Chief Operating Officer (COO), NimbusTech
The cooperative chose a cloud-based ArcGIS environment and made use of ArcGIS’s suite of desktop and mobile applications, including ArcGIS Dashboards and ArcGIS Survey123. NimbusTech helped staff both deploy the GIS and learn how to use it themselves.
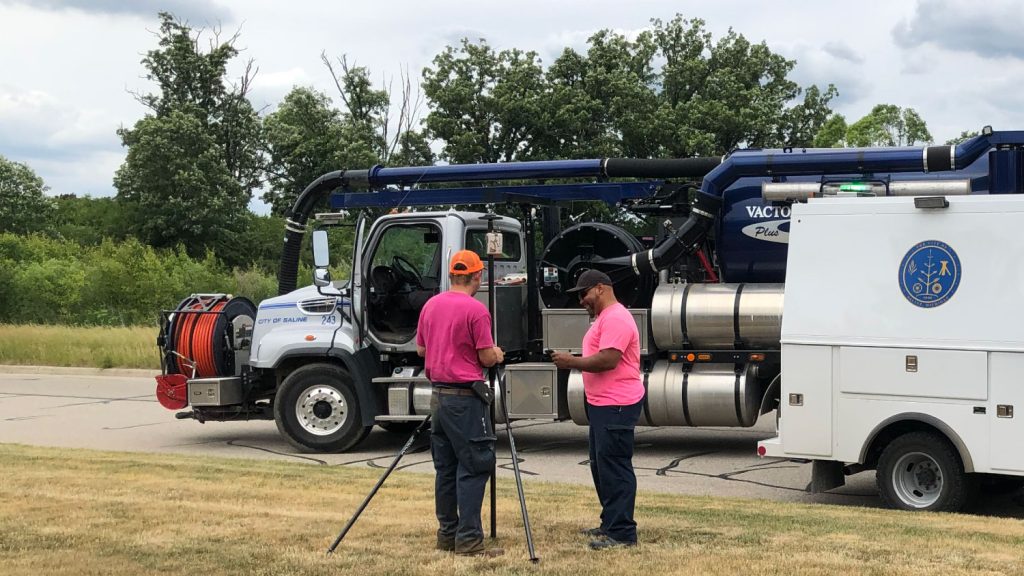
Next, NimbusTech worked with staff to design a new work order system integrated with the GIS. During this process, the need for more precise asset locations emerged. Consequently, a project was launched to collect data on all 52,000 poles associated with their electrical and telecommunications infrastructure.
To meet the need for higher location accuracy, the team deployed global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) equipment from Esri partner Eos Positioning Systems. Previously, the cooperative used the GPS integrated in their consumer tablets, which led to positioning errors. The errors were large enough to negatively impact the accuracy of load analyses on electric lines and other engineering and accounting processes.
By deploying Eos Arrow 100+™ GNSS receivers to field crews, the assets they mapped had around one meter of accuracy. The Arrow 100+ receivers integrated directly with Esri’s ArcGIS Survey123 and ArcGIS Field Maps mobile applications, too. This provided a single, comprehensive, and precise workflow for infrastructure mapping directly into ArcGIS web maps.
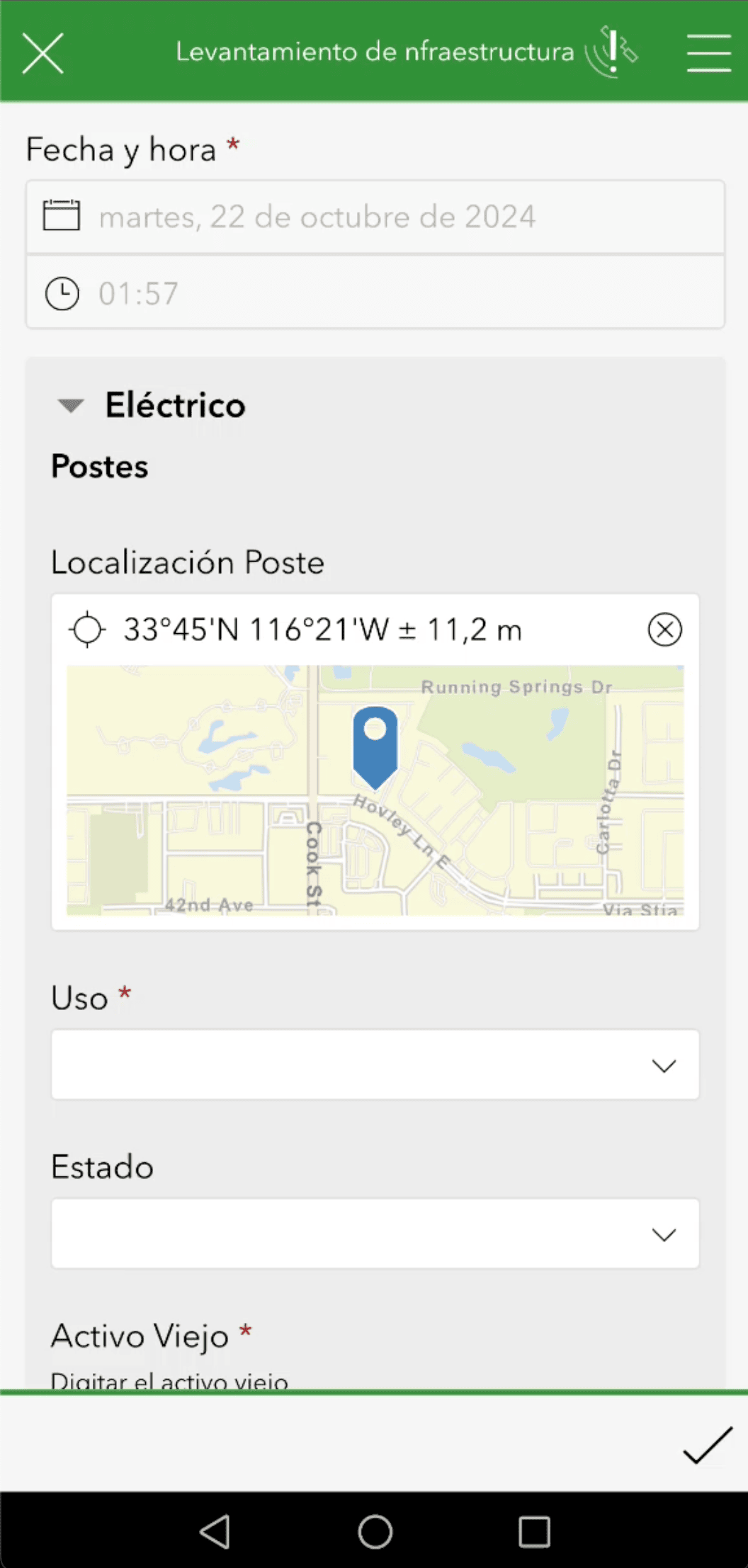
“The integration of Eos Positioning Systems equipment with Survey123 and Field Maps has been crucial for updating the network assets,” said NimbusTech Chief Operating Officer (COO) Clara Abellan. “This proved to be the most effective and cost-efficient option for our client to create an accurate digital twin of their electric system.”
Finally, NimbusTech helped the cooperative migrate onto the ArcGIS Utility Network from a legacy solution. Their plan is to continue updating the Utility Network through 2025.

The Results: Efficiency and Precision
“Today, we can see how GIS technology has helped our cooperative. This has made our work better and faster.”
— Jennifer Camareno, Distribution Network Analysis Engineer, Coopeguanacaste.
Digitally mapping over 52,000 poles has given Coopeguanacaste unprecedented operational efficiency, leading to better decision-making and resource management. The comprehensive GIS allows for quicker response times, optimized load analysis, and improved rate alignment with network performance. Automation now handles much of the task assignment and cost tracking for both electrical and telecommunications services.
Coopeguanacaste’s IT and GIS infrastructure supports accurate asset management, enhanced operational efficiency, and better-aligned electricity rates.
“Today, we can see how GIS technology has helped our cooperative,” said Jennifer Camareno, the Distribution Network Analysis Engineer at Coopeguanacaste. “This has made our work better and faster.”
Coopeguanacaste’s journey from its humble origins in 1965 to becoming a major, competitive cooperative showcases invaluable lessons for organizations seeking to scale services effectively across large, dispersed regions.